Introduction
What is Cloud Computing ? Trying to define cloud computing is not as straight forward as it seems. First we’ll discuss what cloud computing is so that a common understanding is reached. Cloud computing get its name from the cloud network diagram. The cloud icon abstracts all the stuff that makes the Internet (network) work. Cloud computing promotes itself by cutting operational costs and let an organisation focus on strategic projects rather than focusing on keeping a datacenter running. But cloud computing is more than just the Internet. To recap cloud computing is a construct that allows for the access to an application that resides at a location other than your computer or to an Internet-connected device. Mostly the application would be residing in a datacenter. The benefits that emerge from such a construct are quite tangible for example to install an application such as Microsoft Office you either insert a CD or configure a software distribution server, using cloud computing the Microsoft Office installation would already be hosted and handled by the company offering cloud services. For a company to offer cloud computing services mean that that company will host your applications, handle costs of servers, manage software updates and depending on an agreement pay less.
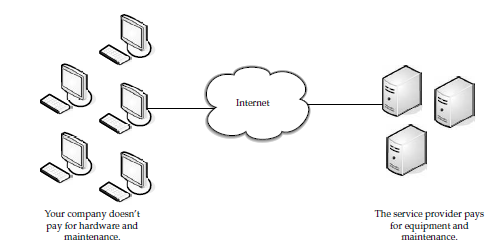
Like everything cloud services have their pros and cons. If you take a look at the diagram above one can easily notice that the lines connecting to Internet are both potential points of failure. When Internet problems occur all the cloud services provided will be down. Application hosted cannot be accessed. This problem is usually countered by allowing local installations for some of the more critical applications.
Components in Cloud Computing
A cloud computing infrastructure is composed from a number of element;

Clients
Clients in a cloud computing setup are the same as that found in current scenarios i.e. normal LANs. Clients are the terminal from which work is done. Clients fall into three categories which are ;
Thin clients are becoming more popular due to the lower hardware costs, security and ease of repair or replacement.
Datacenter
A datacenter is a group of servers which host the applications required by an organisation. A growing trend is virtualised servers which is the creation of multiple servers on one scalable machine through a program called the hypervisor.
Distributed Servers
There are cases were servers are not housed at the same location. Through a cloud computing setup these distributed servers are visible to the end user as one. For example Amazon has multiple datacenters around the world for disaster recovery.
Virtualisation
Virtualisation is a technique by which one or more machines are installed on one machine. This provides a system which all running software is within a virtualised server. This sort of deployment allows for different operating systems to run from the same host server. Virtualisation is relevant to cloud computing since through virtualisation cloud services can be accessed.
Cloud Services
Services offered through cloud computing is the concept with which a company can reuse components from a company offering such services. Services provided are categorised into three main categories;
Software services implies applications hosted as a service which can then be accessed through an internet connection. Using software services through cloud removes maintainability and support for that software from the user’s hands. upgrading of the software is done from the cloud services provider. This type of services can have it’s disadvantages especially when a company requires that a given software needs to be integrated with other software.
Platform services as opposed to software services provide the required resources for application building without having to install them. This type of services is usually required when development, testing or hosting is required by the end-company.
Hardware services is actually the simplest and can be thought of as remote resources. Imagine that instead of buying a server and placing it in your datacenter, said server would be installed, maintained and supported at the company providing the cloud services.
Cloud Services Providers
There are some vendors who offer cloud services. Each vendor varies in the type of services offered as well as their pricing modules.
Amazon
Amazon was one of the very first companies which implemented cloud computing. Some of the services offered by Amazon are;
Amazon’s virtual machines are versions of Linux which might be a bit tough for companies who are used to Microsoft products.
Google
Google offer cloud services through Google’s App Engine. Using App Engine one cannot write a file in his own directory. The file writing feature was removed due to security issues. Writing data must take place in Google’s own database. Google offers online documents, spreadsheets. Developers can build features for these products.
Microsoft
Microsoft’s cloud computing is called Windows Azure. Windows Azure is an operating system that allows organisations to run Windows applications using Microsoft’s datacenters. Azure Services Platform allow for developers to write custom modules for a given company.
Conclusion
My take on Cloud computing is that cloud computing has been with us for quite some time. The only difference is that now big companies are giving it names and offering it to other companies. This doesn’t mean that I find cloud computing to be just a hype on the contrary I find it suitable for certain companies that fall within a certain criteria. For example if a company requires a lot of flexibility in terms of its software and integration with existing applications security problems, speed and reliability become an issue. Also when one is contemplating on working on the cloud one should take into consideration Internet connection speed and reliability. My final point on cloud computing is the legal issues where in lies the concern for the sensitivity of private date. Data protection laws on data hosted on the cloud is freer that data hosted on private server.
What is Cloud Computing ? Trying to define cloud computing is not as straight forward as it seems. First we’ll discuss what cloud computing is so that a common understanding is reached. Cloud computing get its name from the cloud network diagram. The cloud icon abstracts all the stuff that makes the Internet (network) work. Cloud computing promotes itself by cutting operational costs and let an organisation focus on strategic projects rather than focusing on keeping a datacenter running. But cloud computing is more than just the Internet. To recap cloud computing is a construct that allows for the access to an application that resides at a location other than your computer or to an Internet-connected device. Mostly the application would be residing in a datacenter. The benefits that emerge from such a construct are quite tangible for example to install an application such as Microsoft Office you either insert a CD or configure a software distribution server, using cloud computing the Microsoft Office installation would already be hosted and handled by the company offering cloud services. For a company to offer cloud computing services mean that that company will host your applications, handle costs of servers, manage software updates and depending on an agreement pay less.
Network diagram for an organisation offering cloud services
Like everything cloud services have their pros and cons. If you take a look at the diagram above one can easily notice that the lines connecting to Internet are both potential points of failure. When Internet problems occur all the cloud services provided will be down. Application hosted cannot be accessed. This problem is usually countered by allowing local installations for some of the more critical applications.
Components in Cloud Computing
A cloud computing infrastructure is composed from a number of element;
- Clients
- Datacenter
- Distributed servers
Components for a cloud computing solution
Clients
Clients in a cloud computing setup are the same as that found in current scenarios i.e. normal LANs. Clients are the terminal from which work is done. Clients fall into three categories which are ;
- Mobile: Mobile devices like PDA or Smartphones
- Thin: Computers that do not have hard drives and work directly on the datacenter
- Thick: Computer using a web browser to connect to the cloud.
Thin clients are becoming more popular due to the lower hardware costs, security and ease of repair or replacement.
Datacenter
A datacenter is a group of servers which host the applications required by an organisation. A growing trend is virtualised servers which is the creation of multiple servers on one scalable machine through a program called the hypervisor.
Distributed Servers
There are cases were servers are not housed at the same location. Through a cloud computing setup these distributed servers are visible to the end user as one. For example Amazon has multiple datacenters around the world for disaster recovery.
Virtualisation
Virtualisation is a technique by which one or more machines are installed on one machine. This provides a system which all running software is within a virtualised server. This sort of deployment allows for different operating systems to run from the same host server. Virtualisation is relevant to cloud computing since through virtualisation cloud services can be accessed.
Cloud Services
Services offered through cloud computing is the concept with which a company can reuse components from a company offering such services. Services provided are categorised into three main categories;
- Software services
- Platform services
- Hardware services
Software services implies applications hosted as a service which can then be accessed through an internet connection. Using software services through cloud removes maintainability and support for that software from the user’s hands. upgrading of the software is done from the cloud services provider. This type of services can have it’s disadvantages especially when a company requires that a given software needs to be integrated with other software.
Platform services as opposed to software services provide the required resources for application building without having to install them. This type of services is usually required when development, testing or hosting is required by the end-company.
Hardware services is actually the simplest and can be thought of as remote resources. Imagine that instead of buying a server and placing it in your datacenter, said server would be installed, maintained and supported at the company providing the cloud services.
Cloud Services Providers
There are some vendors who offer cloud services. Each vendor varies in the type of services offered as well as their pricing modules.
Amazon
Amazon was one of the very first companies which implemented cloud computing. Some of the services offered by Amazon are;
| Service | Description |
| EC2 | Virtual machines and CPU |
| S3 | Storage up to 5GB in size |
| SQS | Allows for virtualised machines to talk to each other |
| SimpleDB | A web service for running queries on databases in real time. |
Amazon’s virtual machines are versions of Linux which might be a bit tough for companies who are used to Microsoft products.
Google offer cloud services through Google’s App Engine. Using App Engine one cannot write a file in his own directory. The file writing feature was removed due to security issues. Writing data must take place in Google’s own database. Google offers online documents, spreadsheets. Developers can build features for these products.
Microsoft
Microsoft’s cloud computing is called Windows Azure. Windows Azure is an operating system that allows organisations to run Windows applications using Microsoft’s datacenters. Azure Services Platform allow for developers to write custom modules for a given company.
| Service | Description |
| Windows Azure | Provide service hosting and management |
| Microsoft SQl Services | Provides database services and reporting |
| Microsoft .NET Services | Provides a service based .NET framework for development |
| Live Services | Used to share, store unstructured data |
| Microsoft Sharepoint services and Dynamics CRM services | Used for business content and collaboration |
Conclusion
My take on Cloud computing is that cloud computing has been with us for quite some time. The only difference is that now big companies are giving it names and offering it to other companies. This doesn’t mean that I find cloud computing to be just a hype on the contrary I find it suitable for certain companies that fall within a certain criteria. For example if a company requires a lot of flexibility in terms of its software and integration with existing applications security problems, speed and reliability become an issue. Also when one is contemplating on working on the cloud one should take into consideration Internet connection speed and reliability. My final point on cloud computing is the legal issues where in lies the concern for the sensitivity of private date. Data protection laws on data hosted on the cloud is freer that data hosted on private server.